 |
| In spite of the last exploits of the airplanes, the staffs of the terrestrial and maritime forces stay faithful to high altitude observations by kites, to establish their strategy. |
| Winches vehicles |
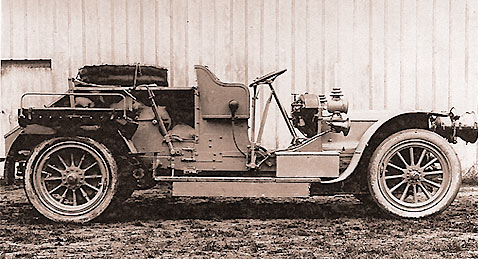
| Captain Saconney improves the winching operations. Manual at first, the winches will become mechanical in 1911, based on motorized vehicles. Convinced of the quality of the equipments designed by the French, Belgium and United States ask France to gear up some of their units. |
 |
 |
Vehicle for winching - type 1911 |
|
 |
 |
| In 1914, Captain Caquot, recovers the mechanism of the old steam winch, called "hot water bottle" ( « bouillotte »). It is driving with a gasoline engine and put on a truck chassis. These are the first winches controlled by Panhard engines. This interim solution became regulation for all companies. |
 |
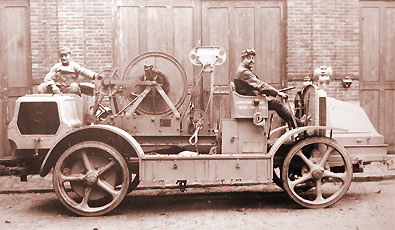
At the same time, Saconney uses the winch he studied for his kites before 1914. He puts it on a chassis Delahaye in 1915 and improves the silhouette of a train of combat with ten companies were equipped with it from August to December 1915. These companies have a car trailer kite and cars tubes for inflating a balloon without discharging the hydrogen tubes. The winch motor Saconney comprises a single motor is used to move the device or the operation of the steel cable. It has two cables, one cable for the ascent of the balloon (5 mm) and a cable 2,000 meters kite with a diameter of 2 mm. Each car company had a small measuring station wind speed and some rubber balloons. |
Treuil automobile Delahaye |
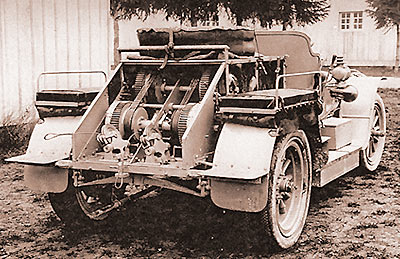
Then succeeded the winch Caquot on chassis Latil, which has two engines for its two functions. The winch known as the " Caquot " was considered the most effective of those that had developed at that time. Since 1911, the company Latil manufactures tractors four-wheel drive and steering, type TAR (Rolling Artillery Tractor), much interest the army to pull guns. It is the first vehicle to be awarded by the Ministry of War in 1913. The ballooning companies are distinguished by their winches car : - From the 1st company to the 24th , the old companies , with their outdated design steam winches - From the 45th to the 54th , mixed companies Saconney ( balloons & Kites ) with winches Saconney - Delahaye - From the 55th to the 94th the Caquot companies with winches Caquot - Latil. |
 |
Treuil caquot à deux moteurs sur tracteur Latil 4 roues motrices modèle 1915 |
| Lucien Frantzen, who in 1907 had founded the fondé l'Union des Cerfs-Volantistes de France (UCVF - kite club) is a volunteer in the first group of ballooning. He joined the automobile kite section of Captain Saconney in Belfort. Each companies benefit from the automobile winches of the kites. The automobile train is composed of an automobile, pulling a van. The attachement is especially flexible; allowing the vehicles to handle very short turns and easily escalate roads with steep hills and tight turns, as the "Ballon d'Alsace" road for example. The average speed is 25 km/h. Each automobile section is composed of 16 men, spanning four teams: 4 mechanics, 4 mooring men (charged with the pilot kite and the nacelle), 4 kite assemblers charged with the even numbered kites, 4 kite assemblers charged with the odd numbered kites. The unit has 12 kites and all the necessary gear to perform an lifting kite. |
 |
Trains de combat de la 55 éme compagnie d'aérostiers en 1915 (photos below) |
|
 |
 |
car in gear - transport aerostatic equipment |
Car telephone office. Non-commissioned officer and an operator are in the office. A liaison officer is usually present. |
 |
 |
car tubes - hydrogen transport |
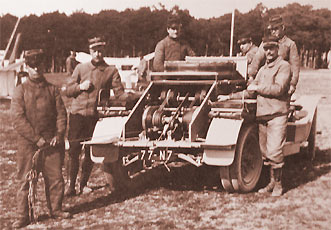
Winches vehicle Saconney |
 |
 |
Winche Saconney |
Winch N° 456 in 1917 |
Of constant tension winches are suitable for the Navy. They can operate with steam, electricity or gas, depending on the different requirements of edge navires. |
|
| Maneuvering winching |
 |
The team is composed of four men : one on each side of the kite to put the kite on rests and attach the kite to the main cable, while the other ties it to the secondary cable. The third man is at the front to clear the different ties; the other is back, operating the winch. The nacelle is then set and a test is made with ballast. |
 |
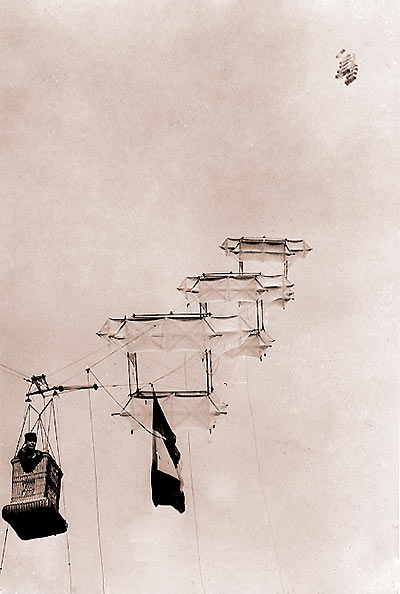
| The launching |
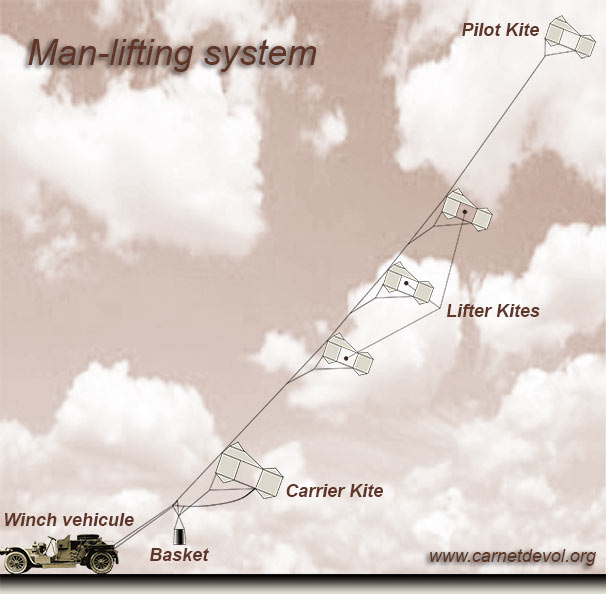
| Le système Saconney comprend deux trains séparés de cerfs-volants. Le train principal, qui tend le câble et le train remorqueur, qui enlève la nacelle. Ce système des deux trains caractérise le type français (photo gauche ci-dessous) et le différencie des trains russes et anglais (ci-dessous, photo de droite). The Saconney system is made of two separated kite trains; one that keeps the main cable under tension and one that raises the nacelle. This system with two trains is characteristic of the French system (photo left below), differentiating it from the Russian and English trains (photo right below). Launching the system (under a minimum wind of 8 m/s) : the head kite is launched first, then successively each kite of the main train. A trained team needs 6 minutes to launch it. Launching conditions: when the wind reaches 10 m/s, seven kites are used (one carrier and six "harness" kites). When the wind reaches 20 m/s, only six are uses; at 30 m/s no ascension is performed. |
 |
 |
| In the event of a cable rupture: several tests are performed by blasting the cable with dynamite charges; the purpose of these tests is to study the dropping speed of the system and set the required number of elements required to ensure the aeronaut's safety. |
| Aerology recordings |
| Captain Saconney 's team continues its aerology recordings with lieutenant Grault (aerial photography) and lieutenant Cholley (mounted kites). Aerology vehicle and maneuvers |
 |
 |
 |
||||||





